“Curious about how does wave energy works? Discover the fascinating mechanics behind this renewable energy source that harnesses the power of ocean waves to generate electricity. Learn about its environmental benefits, reliability, and how it compares to other renewables. Find out why embracing wave energy is crucial for a cleaner and more sustainable future. Read on to explore the world of wave energy and its potential to transform our energy landscape.”
Table of Contents
Introduction
Renewable energy sources have emerged as the key to a future where the necessity for sustainable energy sources is important. Wave energy stands out among them as a possible option that uses the enormous power of the oceans to produce electricity. This essay will describe the operation of wave energy and dig into nine persuasive arguments for why utilizing this renewable energy source is crucial for the globe.
1. The Mechanics of Wave Energy
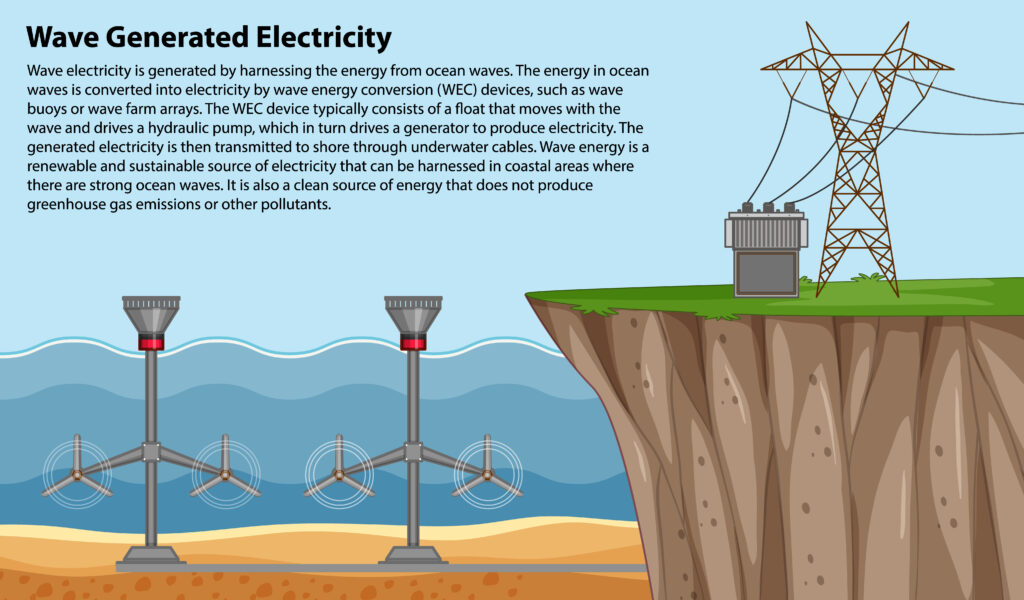
A renewable energy source known as “wave energy” uses the waves’ inherent ability to travel to create power. The process starts when energy from the wind causes waves to develop on the ocean’s surface. These waves convey kinetic energy as they move over the sea.
Offshore, specialized equipment known as wave energy converters is used to harvest this energy. The main objective of these converters, which come in a variety of designs, is to transform the mechanical energy of the waves into electricity. Attenuators, oscillating water columns, and point absorbers are a few typical forms of wave energy converters.
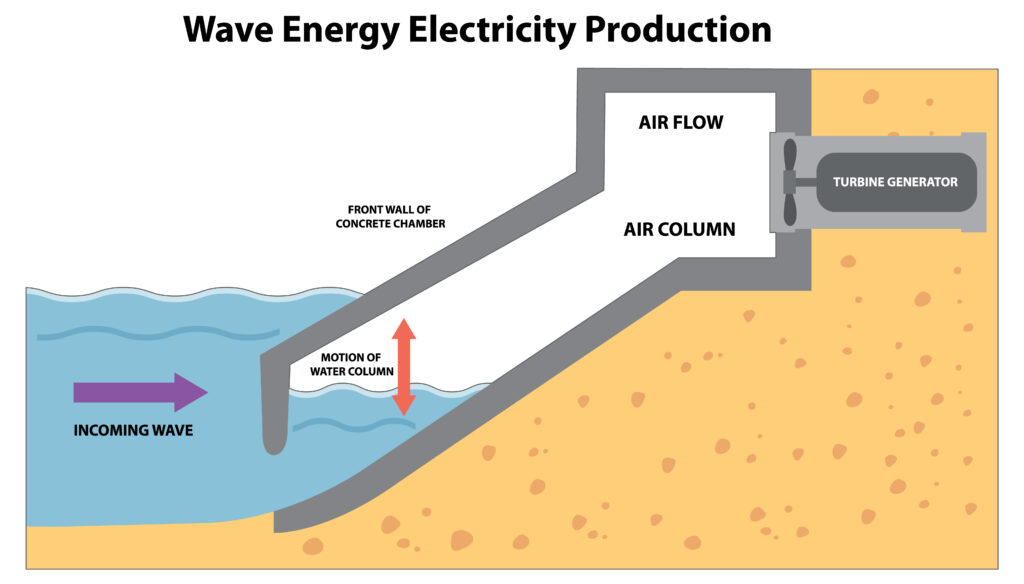
Point absorbers, for instance, are buoy-like objects attached to the seafloor. The buoy moves up and down as the waves pass, and this motion powers hydraulic systems, which transform it into electrical power. However, oscillating water columns have a chamber that is only partially submerged in the water. The air within the chamber moves as a result of the waves, and this airflow powers turbines that are linked to generators to provide energy.
2. Abundance and Reliability

As a result of its reliance on a continuous, natural process, wave energy has enormous potential. Due to the gravitational attraction of the moon and sun, the vast oceans of the Earth continually undergo wave motion. As a result, the amount of wave energy accessible is almost infinite.
Wave energy is far more reliable and steady than other renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Waves are a generally dependable source of power since they occur often and are impacted by weather patterns. This predictability is necessary to provide a constant and reliable supply of power.
3. Environmentally Friendly

The fact that wave energy has no negative environmental impact is one of its most important benefits. Wave energy does not create damaging greenhouse gases, air pollutants, or toxic waste, in contrast to fossil fuel-based power generation. It is a green and clean energy source that has no negative effects on the environment or air quality.
In addition, the use of wave energy converters may potentially benefit the environment. These gadgets may serve as artificial reefs, giving aquatic life a place to thrive. They can improve marine environments where they are deployed by supporting biodiversity and helping to restore habitat.
4. Reduced Carbon Footprint
To reduce our carbon footprint, we must switch from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like wave energy. When burnt for energy, fossil fuels produce substantial volumes of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. These emissions have an impact on climate change and global warming.
We can greatly cut carbon emissions and avert the negative impacts of climate change by utilizing wave energy and other renewable sources. The future of our planet and the welfare of all living things depend on this transition to greener energy sources.
5. Energy Security and Independence
Countries having access to coastal areas benefit from the energy security and independence that wave energy offers. Less reliance on imported fossil fuels lowers exposure to changes in global energy markets and geopolitical concerns.
Coastal countries may use their own wave resources to provide a consistent and independent energy supply. Additionally encouraging national economic stability, this energy independence lessens the effects of fluctuating energy prices on consumers and businesses.
6. Job Creation and Economic Growth

Numerous job possibilities are created across a variety of industries as a result of the development and operation of wave energy projects. It takes expert personnel in engineering, manufacturing, construction, and maintenance to build and maintain wave energy converters.
Economic growth may be boosted by investing in wave energy, especially in coastal areas. The creation of jobs in this industry can strengthen regional economies and give communities access to work. Additionally, wave energy research and development can spur creativity and technical growth.
7. Long-Term Cost Efficiency
Although wave energy projects may have greater initial setup costs than conventional fossil fuel-based facilities, the long-term advantages make it an economically sensible choice. When compared to traditional power plants, wave energy systems have comparatively low operating and maintenance expenses.
Moreover, it is probable that the prices of producing wave energy will continue to drop as technology develops and economies of scale take hold. Wave energy is a desirable option for producing sustainable energy because of its economic effectiveness and favorable environmental effects.
8. Offshore Advantages

Projects for wave energy are often situated offshore, far from crowded regions. Wave energy converters have a relatively modest footprint and are less invasive on coastal land usage than certain land-based renewable energy projects that may need large land expanses.
Offshore placement makes wave energy projects less visually intrusive and less likely to clash with already-existing land uses. They may also live in harmony with other maritime activities including tourism, fishing, and shipping.
9. Diversification of Energy Portfolio
Energy portfolio diversification is essential for guaranteeing energy stability and security. A nation becomes more susceptible to supply interruptions and price swings when it depends only on one energy source, particularly fossil fuels.
The addition of wave energy to the energy mix diversifies the sources used to produce electricity. This diversification strengthens the energy system’s resilience since various sources may work well together under a variety of weather conditions or energy needs.
Conclusion
A potential and creative approach to meet our energy demands responsibly is wave energy. It is an appealing choice for a more sustainable future because to its quantity, dependability, and eco-friendliness. We can make a substantial contribution to reducing climate change and ensuring a cleaner, more sustainable environment for future generations by embracing wave energy and expanding its use globally. In order to ensure the welfare of our planet and its people, it is essential that we give renewable energy sources, such as wave energy, top priority.
frequently asked questions (FAQ) about wave energy:
1. What is wave energy, and how does it work?
Wave energy is a renewable energy source that harnesses the natural movement of ocean waves to generate electricity. Specialized devices called wave energy converters are deployed offshore, where they capture the kinetic energy from the rising and falling of waves. This mechanical energy is then converted into electrical power through various conversion technologies, providing a clean and sustainable energy source.
2. Is wave energy a reliable source of power?
Yes, wave energy is considered a reliable source of power. Unlike some other renewable energy sources like solar and wind, waves tend to be more predictable and stable. The Earth’s oceans are constantly in motion due to the gravitational forces of the moon and the sun, ensuring a continuous supply of wave energy. As a result, wave energy can provide a consistent and steady power generation, making it a reliable option for sustainable electricity production.
3. What are the environmental benefits of wave energy?
Wave energy is an environmentally friendly power source. Unlike fossil fuel-based power plants, wave energy does not produce greenhouse gases, air pollutants, or hazardous waste. By using wave energy, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and contribute to mitigating climate change. Additionally, the deployment of wave energy converters can create artificial reefs, promoting marine biodiversity and supporting habitat restoration.
4. How does wave energy compare to other renewable energy sources?
Wave energy has several advantages compared to other renewable energy sources. While solar and wind power require specific weather conditions and land availability, wave energy is abundant in coastal regions and has higher predictability. Wave energy also offers a more constant power generation compared to solar and wind, which can fluctuate based on weather patterns. Moreover, wave energy’s offshore placement reduces visual impact and land use conflicts.
5. Are there any challenges associated with wave energy implementation?
Although wave energy shows great promise, there are still some challenges to overcome for widespread implementation. One of the main challenges is the high initial setup costs, including research, development, and deployment of wave energy converters. Additionally, the harsh marine environment can cause wear and tear on the devices, requiring regular maintenance. However, ongoing advancements in technology and increased investment are addressing these challenges, making wave energy a more viable and attractive option for renewable power generation.

